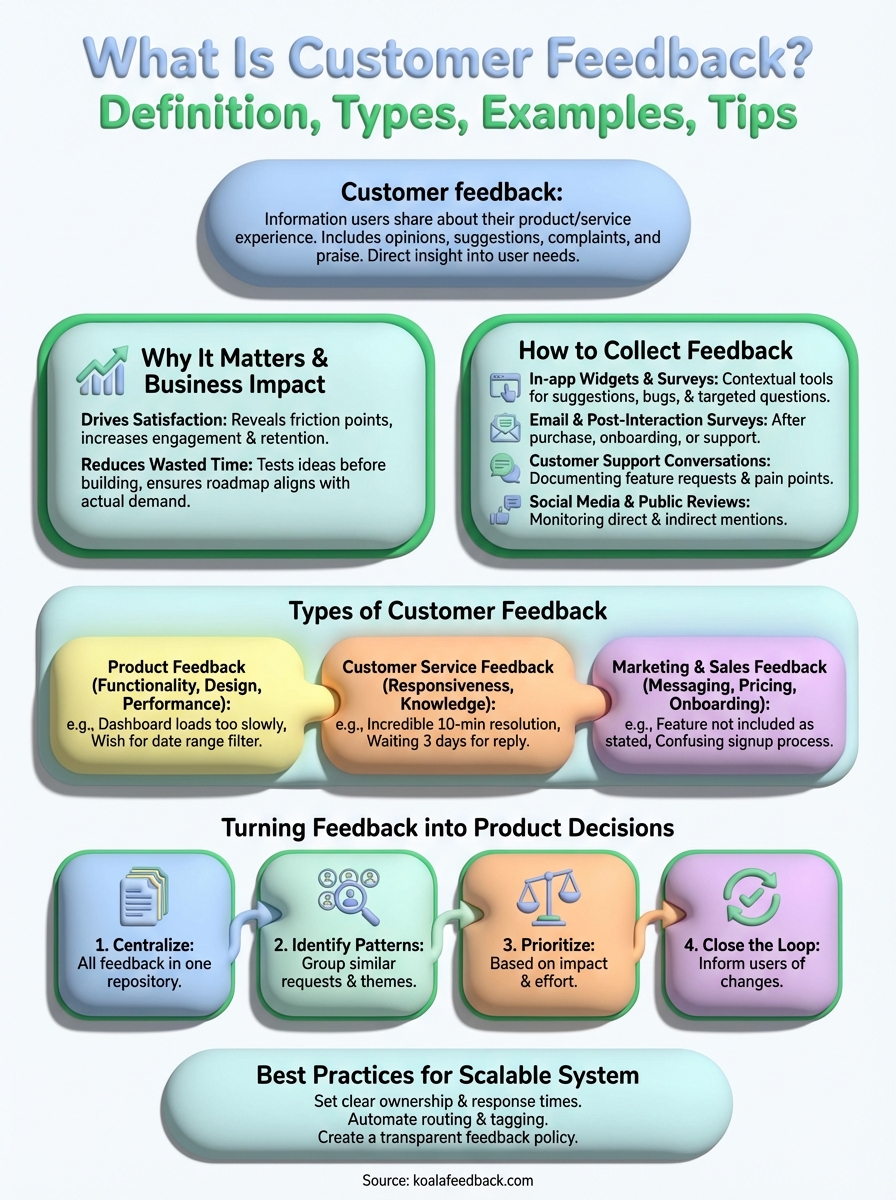
Customer feedback is information your users share about their experience with your product or service. It includes their opinions on features, suggestions for improvements, complaints about problems, and praise for what works well. This feedback gives you direct insight into what your customers think, need, and expect from your product. Without it, you're guessing at what to build next.
This guide covers everything you need to know about customer feedback. You'll learn why feedback drives business growth, practical methods for collecting it from multiple channels, and the main types you'll encounter with real examples. We'll walk you through how to analyze and prioritize feedback to make smarter product decisions, plus share best practices for building a feedback system that scales with your company. By the end, you'll know exactly how to turn customer feedback into products your users actually want and features that move your business forward.
Customer feedback directly impacts your bottom line and product success. When you understand what is customer feedback and act on it, you make decisions based on real user needs instead of assumptions. This approach reduces the risk of building features nobody wants and helps you allocate resources to improvements that actually matter to your customers.

Feedback shows you which features keep users engaged and which ones frustrate them. You'll discover friction points in your user experience before they cause widespread churn. Users tell you exactly where they struggle, what they love, and what would make your product indispensable to them. This insight helps you prioritize development around features that increase retention and satisfaction.
Customer feedback turns guesswork into strategy by giving you direct access to user needs and expectations.
Building features without validation wastes your team's time and budget. Feedback helps you test ideas before committing engineering resources to them. You can validate whether a proposed feature solves a real problem for multiple users or if it's just a one-off request. This process ensures your roadmap aligns with actual demand, not internal opinions or competitor copying.
You need multiple channels to capture feedback because your users share insights in different ways and at different moments. Some users actively seek out feedback forms, while others drop casual comments during support conversations or on social media. Understanding what is customer feedback means recognizing that it flows through various touchpoints, and you should capture it wherever it appears. A strong collection strategy combines both active methods (where you ask directly) and passive methods (where you listen to unsolicited input).
Place feedback widgets directly inside your product where users spend their time. These contextual tools let users submit suggestions, report bugs, or share opinions without leaving your application. You can trigger targeted surveys based on specific actions, like after completing a workflow or using a new feature. This approach captures feedback while the experience is fresh in your user's mind, leading to more accurate and detailed responses.

Collecting feedback inside your product generates higher response rates and better quality insights than external surveys.
Send surveys after key moments in the customer journey, such as completing a purchase, finishing onboarding, or closing a support ticket. Email surveys work well for gathering broader feedback about satisfaction levels or feature requests. Keep these short with clear questions that take less than two minutes to complete. The timing matters more than the length of your survey, so send them when the interaction is still recent but not immediately disruptive.
Your support team collects valuable feedback during every conversation with users. Train your team to document feature requests, pain points, and compliments they hear during ticket resolutions and live chats. Support interactions reveal urgent problems and common frustrations that might not surface in formal surveys. Set up a system where your support team can tag and categorize this feedback so it reaches your product team automatically.
Monitor mentions of your brand on social platforms, review sites, and forums where your users gather. Users often share honest opinions publicly before they contact your support team. Track both direct mentions (where users tag you) and indirect discussions (where they talk about your product without tagging you). This unsolicited feedback shows you what users truly think and how they describe their experiences to peers.
Customer feedback falls into distinct categories based on what aspect of your business users are commenting on. When you understand what is customer feedback in each category, you can route it to the right team and take appropriate action. Each type requires different handling and reveals specific insights about your product, service, or business operations. You'll encounter these three main types most frequently in your feedback collection efforts.

Product feedback addresses your actual product or service. Users share opinions about feature functionality, user interface design, performance issues, and missing capabilities they need. This feedback type directly informs your product roadmap and development priorities.
Examples include:
Customer service feedback evaluates your support team's responsiveness, knowledge, and helpfulness. Users comment on how quickly you resolve issues, whether your team understands their problems, and the overall quality of their support interactions. This feedback helps you improve your support processes and training programs.
Examples include:
Route customer service feedback to your support leadership team so they can identify training needs and process improvements.
Marketing and sales feedback covers your messaging accuracy, pricing structure, onboarding experience, and buying process. Users tell you whether your marketing materials set accurate expectations, if your pricing makes sense, and how smooth their purchase journey felt. This feedback reveals gaps between what you promise and what you deliver.
Examples include:
Collecting feedback means nothing if you can't convert it into actionable product improvements. Understanding what is customer feedback involves more than just gathering information; you need a systematic process to analyze, prioritize, and act on user input. The gap between collecting feedback and shipping features users want often comes down to how you organize and evaluate what you hear. Your process should connect raw user comments directly to your roadmap decisions, creating a clear path from customer voice to product development.
Feedback scattered across email threads, support tickets, spreadsheets, and chat logs creates chaos and missed insights. You need one central repository where your entire team can access, search, and reference all customer feedback. This system should automatically capture feedback from multiple channels and organize it by theme, user, or request type. When everything lives in one place, you spot recurring patterns faster and prevent duplicate work on similar requests.
Raw feedback often arrives in different words describing the same underlying need. Review your centralized feedback regularly to identify common themes and group related requests together. One user might ask for "better reporting," another for "custom dashboards," and a third for "data export options" when they all want more visibility into their metrics. Grouping similar feedback shows you the real scope of demand for specific improvements and helps you understand the root problem users need solved.
Patterns in feedback reveal the difference between one user's unique request and a widespread need that deserves development resources.
Not all feedback deserves immediate action. Evaluate each grouped request using impact (how many users need this and how much value it creates) and effort (engineering time and complexity required). High impact, low effort improvements should rise to the top of your roadmap. Consider factors like how many users requested the feature, their account value, alignment with your product vision, and whether solving this problem helps you acquire or retain customers.

Tell users when their feedback leads to product changes. Send notifications when you start building requested features and again when you ship them. This communication builds trust and shows users their input matters to your team. Users who see their suggestions implemented become advocates who submit more feedback and stick with your product longer. Even when you decide not to build something, explain why so users understand your reasoning.
Your feedback system needs to grow with your company without creating bottlenecks or overwhelming your team. Understanding what is customer feedback at scale means building processes and tools that handle increasing volume while maintaining quality and responsiveness. A scalable system ensures no feedback gets lost, users receive timely responses, and your product team can access insights without digging through endless comments. The right infrastructure turns feedback collection from a manual burden into an automated advantage that improves as your user base expands.
Assign specific team members to manage feedback categories and establish response time commitments. Product managers might own feature requests, support leads handle service issues, and marketing teams address messaging concerns. Define how quickly you'll acknowledge new feedback (within 24 hours works for most teams) and when you'll provide substantive updates on status changes. Clear ownership prevents feedback from sitting unaddressed and gives users confidence their input reaches the right people.
Response time expectations set user trust levels and determine whether customers continue sharing valuable insights with your team.
Use tools that automatically categorize incoming feedback by type, sentiment, or product area. Automation reduces manual work sorting through hundreds of comments and ensures urgent issues surface immediately. Set up rules that route bug reports to your engineering team, billing questions to finance, and feature requests to product management. Smart tagging helps you filter and search feedback later when making roadmap decisions or analyzing trends across user segments.
Publish a clear policy explaining how you collect, review, and use customer feedback. Tell users what happens after they submit feedback, realistic timelines for responses, and how you decide what to build. Transparency manages expectations and encourages more users to participate in your feedback process. Your policy should also explain what feedback you prioritize and why, helping users understand that not every request becomes a feature but every suggestion gets considered.
Customer feedback transforms how you build products by connecting development decisions directly to user needs. When you understand what is customer feedback and implement a system to collect, analyze, and act on it, you stop guessing and start building features your users actually want. This approach reduces wasted development time, increases customer satisfaction, and helps you prioritize resources on improvements that drive retention and growth.
Start capturing feedback from your users today with a centralized system that scales with your business. Koala Feedback helps you collect user input, prioritize feature requests, and share your product roadmap in one platform. Your customers have the answers to your product questions, you just need the right tools to listen and respond effectively.

Start today and have your feedback portal up and running in minutes.